Joanne Hovis on Business Plans for Municipal Fiber
Joanne Hovis, President of CTC Technology and Energy, recently published a must-read article in Broadband Properties Magazine. Whether you are a community leader investigating the possibility of a publicly owned network or an engaged citizen looking for pros and cons, this piece explains practical benefits succinctly. In her article, The Business Case For Government Fiber Networks [PDF], Hovis looks at life beyond stimulus funding. She points out how we should evaluate municipal networks in an environment where shareholder profit is not the first consideration.
Hovis gives a brief history of how local communities reached this point of need. As many of our readers know, local communities used to be able to negotiate with cable providers for franchise opportunities and rights-of-way. Often cable providers would construct broadband infrastructure in exchange for a franchise to operate in a given community, creating I-Nets for local government, schools and libraries. Once states inserted themselves into the process with state-wide franchising, local negotiating power evaporated. Many of those franchise agreements are ending and local leaders are considering municipal fiber optic networks.
Hovis stresses that municipalities do not function in the same environment as the private sector. While they still have a fiscal responsibility to their shareholders (the taxpayers) the main function is providing public safety, encouraging economic development, offering education, and using tax dollars to better the quality of life. Hovis describes how redefining return on investment (ROI) needs to go beyond the balance sheet bottom line.
These benefits have nothing to do with traditional financial measures. Rather, they represent the return to the community in terms of such largely intangible societal benefits as enhancing health care quality, narrowing the digital divide, providing enhanced educational opportunities to school children, delivering job search and placement opportunities at public computer centers and helping isolated senior citizens make virtual social connections.



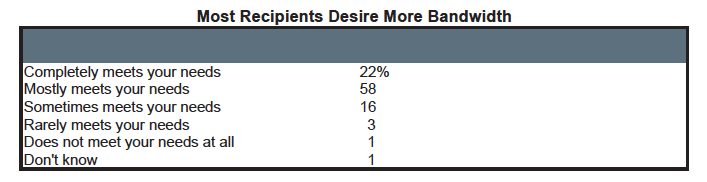 The question is why they want faster connections. Only 20% say their current connection completely meets their need to conduct online testing and assessment applications - with another 44% saying it "mostly" meets those needs.
The question is why they want faster connections. Only 20% say their current connection completely meets their need to conduct online testing and assessment applications - with another 44% saying it "mostly" meets those needs.
 These gaps represent a tremendous opportunity for growth - communities should be building their own fiber-optic connections to connect these key institutions and ensure they will have affordable, fast, and reliable connections well into the future. By owning the network, these institutions will have greater control over future costs and their capacity to take advantage of even newer applications.
The FCC should favor locally owned networks to encourage self-reliance instead of never-ending subsidies to private carriers who have little incentive to lower prices and increase investment.
These gaps represent a tremendous opportunity for growth - communities should be building their own fiber-optic connections to connect these key institutions and ensure they will have affordable, fast, and reliable connections well into the future. By owning the network, these institutions will have greater control over future costs and their capacity to take advantage of even newer applications.
The FCC should favor locally owned networks to encourage self-reliance instead of never-ending subsidies to private carriers who have little incentive to lower prices and increase investment.
